- Repeat expansions are common genetic variations that are usually associated to neurogenetic disorders. These expansions are a different class of genetic disease that occur due to dynamic mutations that can change from generation to generation.
- Conditions that are caused by repeat expansions are characterized by unstable expansions of gene segments that consist of repeating unites of three or more nucleotides.
- PCR-based screening of repeat lengths is the gold standard assessment of diseases associated with expansion repeats.The Repeat Expansion Detection test is usually done by PCR or Southern Blot.
EXP – Expansion Repeats

Expansion repeats testing is indicated when individuals present with diagnostic or clinical symptoms relating to diseases caused by expansion repeats. This test can be offered in all life stages depending on clinical presentation
The most common genetic disorders detected by Expansion repeat testing include:
- CAG/polyQ diseases
- Spinocerebellar ataxia types SCA1, SCA2, SCA3, SCA6, SCA7, SCA8, SCA10, SCA12, SCA31, SCA10
- C9ORF72 frontotemporal dementia/ amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
- Huntington disease
- Myotonic dystrophy types 1 and 2
- Oculopharyngeal muscular dystrophy
- Fragile X tremor ataxia syndrome
- Friedreich Ataxia
- Fragile X syndrome
- Myoclonic epilepsy
Depending on the type of suspected disorder there are different types of PCR tests that can be offered.
- When disorder is caused by a small number of repeats (< 50 repeats), amplification primers encompass the repeat.
- When a disorder is caused by a large number of repeats (>100 repeats), that conventional PCR cannot amplify. Amplification primers encompass the repeat and include the repeated sequence.
-
Negative Result
A negative results indicates that the individual has the normal alleles repeats in the target gene and is not at an increased risk of developing the disorder.
-
Premutation Alleles:
A pre-mutation is a change that is of intermediate risk or in a “grey area”. Individuals with pre-mutations have a higher than normal number of repeat expansion but less than the number expected of the full mutation. The risk of an individual with a pre-mutation is variable and these pre-mutations are identified in such a manner because there is a small chance that they are unstable and may expand to a full mutation in future generations. There is no reported risk for an individual with an intermediate sized allele to have a child with a full mutation. Traditionally, a carrier of a genetic mutation is defined as a person who inherits an altered form of a gene but shows no effects of that mutation. However, this does not necessarily apply in cases with expansion repeats as depending on the condition, individuals with a pre-mutation might present with symptoms.
-
Full mutation/ Disease-Causing Alleles:
A result of a full mutation indicates that the individual has the expansion repeats that would cause genetic disease and this individual is likely to have symptoms of the disorder. Reduce penetrance plays a role in some expansion repeat diseases and so individuals with the full mutation may have variable symptoms depending on the condition in question.
Sample Requirements
For genetic testing through next generation sequencing, the following sample types are accepted. A thorough labelling of the tube with unique identifying information is suggested, incorrect labelling can lead to rejection of the sample. The minimum required information to identify and accept a sample is – Patient’s full name, Date of birth, Gender and Medical Record Number.
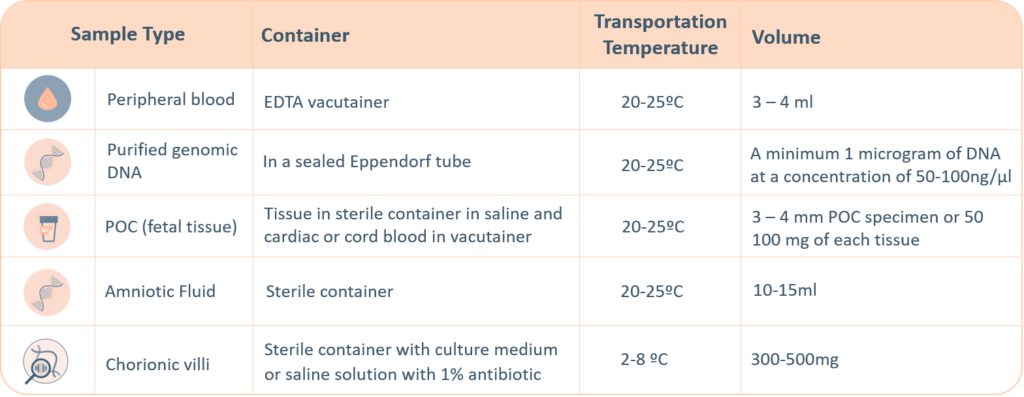
- Maternal blood sample must be sent with all products of conception, CVS and Amnio samples
- Precedence will be given to all prenatal samples
The ‘informed consent’ form and the ‘test requisition from’ (included within the provided kit) must be properly filled-in and signed by the patient and sent with the samples inside the shipping box or by e-mail to the laboratory. Igenomix will send you all the documents needed for the pick-up and transportation of the appropriate kit to our laboratory
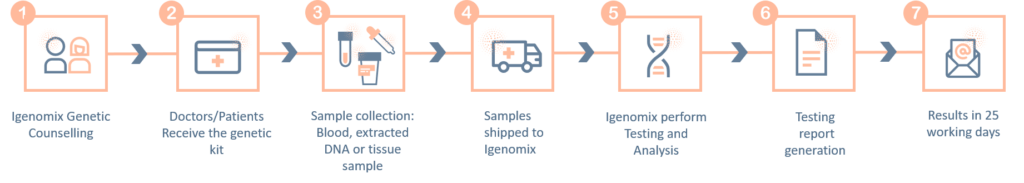
Methodology
Limitations
- The scope of this assay is limited to the repeat expansion analysis of the targeted gene and may not reveal the exact number of repeats present in large expansions.
- Gene sequencing and deletion/duplication analysis are not included in this assay but can be ordered separately.
- This analysis does not include methylation studies.
Why Choose IGENOMIX?
High-Quality interpretation
Genetic counselling E-learning platform
Easy & Fast Online tests management
Local Labs over the Middle East
All Technical capabilities In-House
100% In-House sequencing and Bio IT
CAP & ISO accredited lab
Using international, population and
diseases Databases, including HGMD





