- Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia (HHT) is also known as Osler-Weber-Rendy disease or syndrome and is associated with the formation of abnormal blood vessels in the mucous membrane, body organs and skin. This condition is a rare genetic condition that is associated with autosomal dominant inheritance. It is caused by variations in the genes that are associated with developing the connection between the arteries and the veins – arteriovenous malformations (AVM). the severity of this condition can vary greatly within individuals in the population and in the family. One of the main characteristics of HHT is spontaneous nosebleeds that can affect the quality of life and cause iron deficiency anemia
- Specialties involved – Hematology, dermatology, ENT
Hematology
Sample Requirements
For genetic testing through next generation sequencing, the following sample types are accepted. A thorough labelling of the tube with unique identifying information is suggested, incorrect labelling can lead to rejection of the sample. The minimum required information to identify and accept a sample is – Patient’s full name, Date of birth, Gender and Medical Record Number.
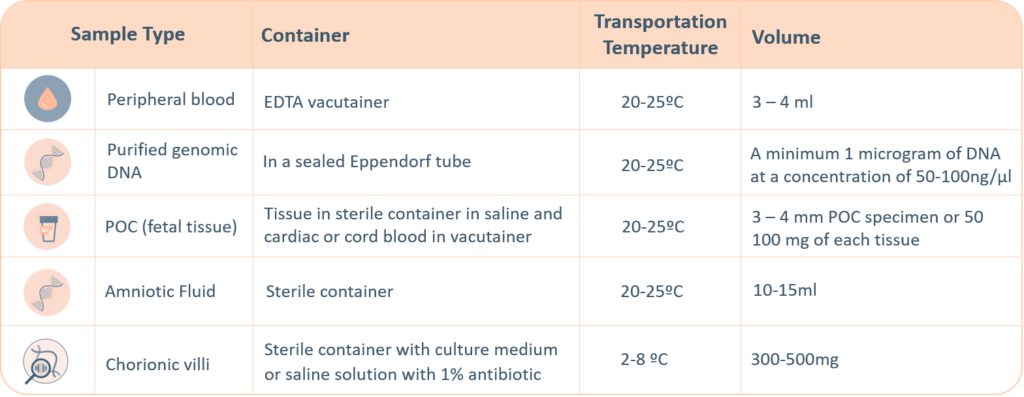
- Maternal blood sample must be sent with all products of conception, CVS and Amnio samples.
- Precedence will be given to all prenatal samples.
The ‘informed consent’ form and the ‘test requisition from’ (included within the provided kit) must be properly filled-in and signed by the patient and sent with the samples inside the shipping box or by e-mail to the laboratory. Igenomix will send you all the documents needed for the pick-up and transportation of the appropriate kit to our laboratory
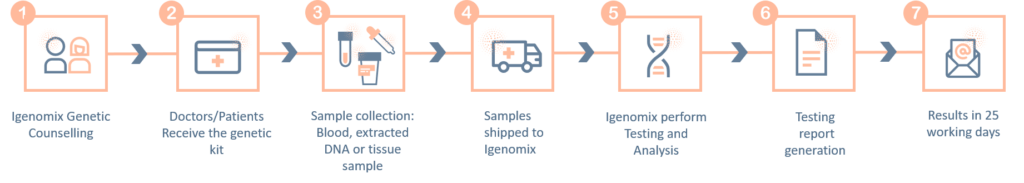
Methodology
Limitations
The probes used for this test are designed to detect known genes in the curated panel. Therefore, this test is unable to detect genes not defined by the NCBI reference genome GRCh37 or non-human genome sequences including viral sequences or non-nuclear DNA that are designated in the specific panel.
In addition, due to the limitations of NGS technologies, the following variants cannot be readily detected: large deletions/duplications greater than 40 base pairs, copy number variations, homopolymer stretches, variants in pseudogene regions, gene fusions, balanced translocations, inversions, ploidy changes, uniparental disomy, and repeat expansion regions.
Furthermore, variants present outside the exons (non-coding region) could be missed; these variants can affect gene activity and protein production which may lead to genetic disorders. This technique does not cover the entire exome, (the % of bases with coverage above 20x is approximately 97%). It may not be possible to resolve certain details about variants such as mosaicism, phasing, or mapping ambiguity.
Analytical limitations may also occur due to the provided clinician information. Accurate and thorough clinical information of the patient(s) and family members is required as incomplete information may lead to false positive or negative results
This list of indications and symptoms is not necessarily a comprehensive list and only covers common symptoms associated with disease, signs and symptoms should be discussed with your physician. If you feel like you are affected by one or more of these syndromes visit a doctor immediately. The information presented in this site is not meant to diagnose any medical or genetic condition rather give an overview of the panels presented and offer guidance as to which panel is most appropriate. The associated diseases listed are not necessarily a comprehensive list – more diseases may be added to this list as new information about the disease and the genes associated with these diseases and panels arises
Why Choose IGENOMIX?
High-Quality interpretation
Genetic counselling E-learning platform
Easy & Fast Online tests management
Local Labs over the Middle East
All Technical capabilities In-House
100% In-House sequencing and Bio IT
+ CAP & ISO accredited lab
Using international, population and
diseases Databases, including HGMD





